Nucleotide second messenger signaling
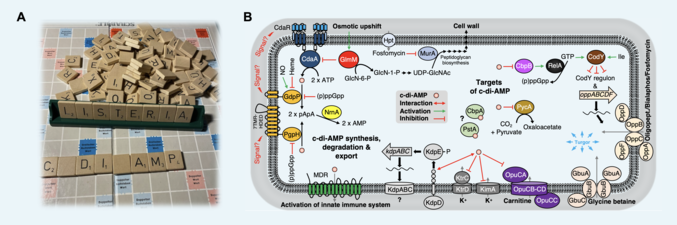
Cyclic diadenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is a signaling nucleotide that has been discovered 15 years ago. The human pathogenic bacterium Listeria monocytogenes played a central role in elucidating the biological function of c-di-AMP (Figure A) (Schwedt et al., 2023). Five classes of c-di-AMP-synthesizing cyclases are known, among them the most-abundant cyclase CdaA. c-di-AMP can also be degraded by specific phosphodiesterases (Figure B). Several c-di-AMP targets have been identified. Some targets are involved in the uptake and export of osmolytes like potassium ions (Figure B). c-di-AMP is in fact essential to prevent the uncontrolled influx of osmolytes into bacterial cells (Gundlach et al., 2017). Recently, we have observed that c-di-AMP also assists osmoadaptation of L. monocytogenes by modulating the activities of two potassium transporters (Figure B) (Gibhardt et al., 2019). Thus, the c-di-AMP–dependent control of potassium homeostasis seems to be conserved among phylogenetically related bacteria. L. monocytogenes possesses only the diadenylate cyclase CdaA, which has been biochemically and structurally characterized (Rosenberg et al., 2015). We have also shown that the activity of the L. monocytogenes diadenylate cyclase CdaA is modulated by the membrane-attached CdaR protein (Figure B) (Gibhardt et al., 2020). Moreover, the essential phosphoglucosamine mutase GlmM, which is required for cell wall synthesis, moonlights in controlling the activity of CdaA in L. monocytogenes. Currently, we are working on the regulation of CdaA. Our goal is to unravel how bacteria sense the environmental osmolarity.
Selected publications
Gibhardt J, Commichau FM (2025) c-di-AMP is an envoy of inflammation. Nat Chem Biol. 21: 1132-1133.
Bhowmick S, Viveros RP, Latoscha A, Commichau FM, Wrede C, Tschowri N (2024) Cell shape and division septa positioning in filamentous Streptomyces requires a functional cell wall glycopolymer ligase CglA. mBio. 9:e0149224.
Schwedt I, Wang M, Gibhardt J, Commichau FM (2023) Cyclic di-AMP, a multifaceted regulator of central metabolism and osmolyte homeostasis in Listeria monocytogenes. µLife, 4: uqad005.
Wang M, Wamp S, Gibhardt J, Holland G, Schwedt I, Schmidtke KU, Scheibner K, Halbedel S, Commichau FM (2022) Adaptation of Listeria monocytogenes to perturbation of c-di-AMP metabolism underpins its role in osmoadaptation and identifies a fosfomycin uptake system. Environ Microbiol. 24: 4466-4488.
Gibhardt J Heidemann JL Bremenkamp R Rosenberg J Seifert R Kaever V Ficner R Commichau FM (2020) An extracytoplasmic protein and a moonlighting enzyme modulate synthesis of c-di-AMP in Listeria monocytogenes Environ Microbiol 22: 2771-2791.
Commichau FM Heidemann JL Ficner R Stülke J (2019) Making and breaking of an essential poison: the cyclases and phosphodiesterases that produce and degrade the essential second messenger cyclic di-AMP in bacteria. J Bacteriol 201: pii: e00462-18.
Gibhardt J Hoffmann G Turdiev A Wang M Lee VT Commichau FM (2019) c-di-AMP assists osmoadaptation by regulating the Listeria monocytogenes potassium transporters KimA and KtrCD. J Biol Chem 294: 16020-16033.
Quintana IM Gibhardt J Turdiev A Hammer E Commichau FM Lee VT Magni C Stülke J (2019) The KupA and KupB proteins of Lactococcus lactis IL1403 are novel c-di-AMP resceptor proteins responsible for potassium uptake. J Bacteriol 201: e00028-19.
Commichau FM Gibhardt J Halbedel S Gundlach J Stülke J (2018) A delicate connection: c-di-AMP affects cell integrity by controlling osmolyte transport. Trends Microbiol 26: 175-185.
Gundlach J Herzberg C Kaever V Gunka K Hoffmann T Weiß M Gibhardt J Thürmer A Hertel D Daniel R Bremer E Commichau FM Stülke J (2017) Control of potassium homeostasis is an essential function of the second messenger cyclic di-AMP in Bacillus subtilis. Sci Signal 10: pii: eaal3011.
Rismondo J Gibhardt J Rosenberg J Kaever V Halbedel S Commichau FM (2016) Phenotypes associated with the essential diadenylate cyclase CdaA and its potential regulator CdaR in the human pathogen Listeria monocytogenes. J Bacteriol 198: 416-26.
Rosenberg J Dickmanns A Neumann P Gunka K Arens J Kaever V Stülke J Ficner R Commichau FM (2015) Structural and biochemical analysis of the essential diadenylate cyclase CdaA from Listeria monocytogenes. J Biol Chem 290: 6596-6606.
Commichau FM Dickmanns A Gundlach J Ficner R Stülke J (2015) A jack of all trades: the multiple roles of the unique essential second messenger cyclic di-AMP. Mol Microbiol 97: 189-204.
Further information
The project was funded by the DFG in the framework of the SPP1879 that is coordinated by Prof. Dr. Regine Hengge (HU Berlin).